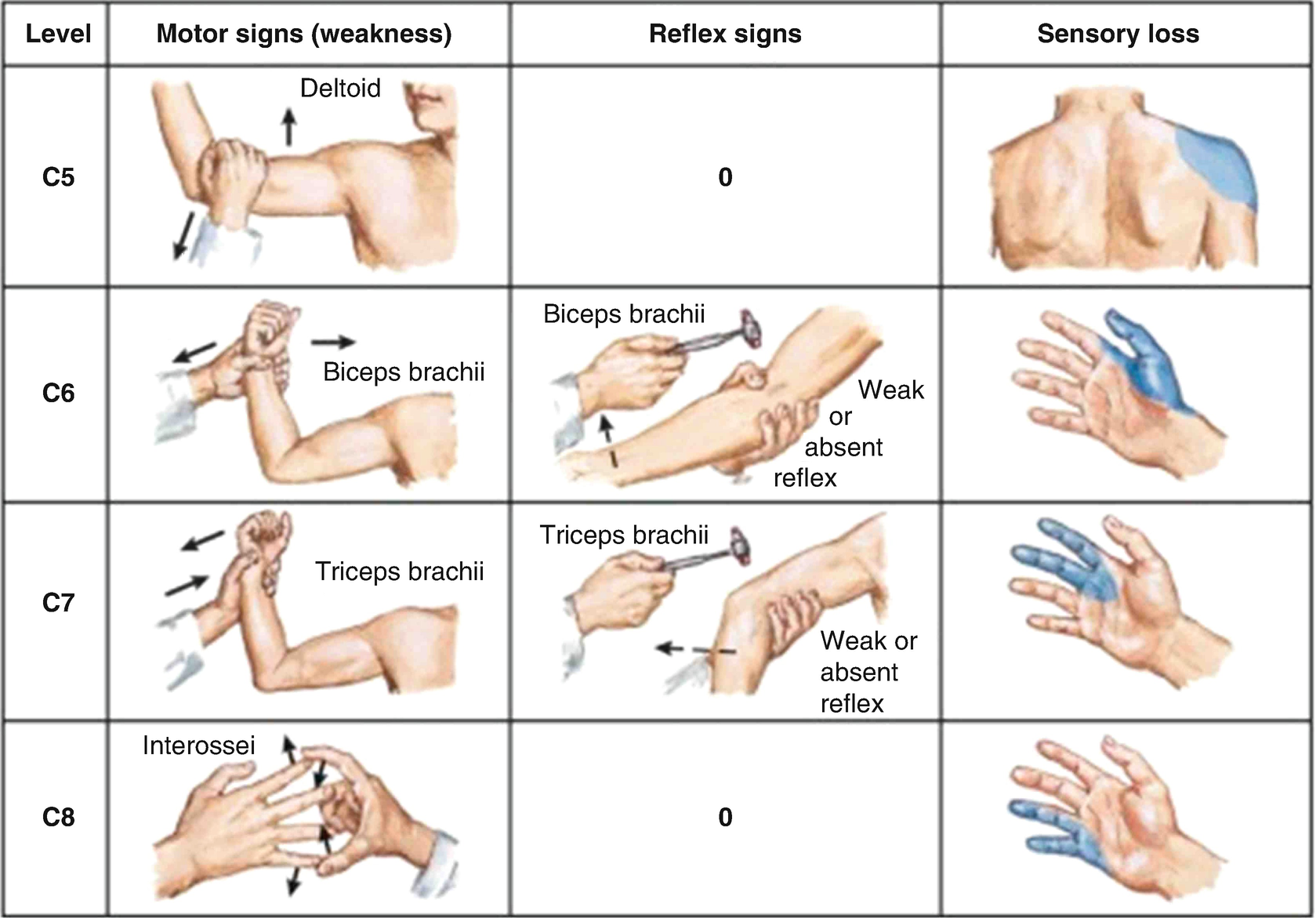
Positive hoffman's sign and hyperreflexia 226242
A positive Babinski sign is considered a pathological sign of upper motor neuron disease except for infants, in whom it is normal, whereas a positive Hoffmann's sign can be present in an entirely normal patient A positive Hoffmann's sign in the normal patients is more commonly found in those who are naturally hyperreflexive (eg 3 reflexes) A positive Hoffmann's sign is a worrisomeHyperreflexia refers to hyperactive or repeating (clonic) reflexes These usually indicate an interruption of corticospinal and other descending pathways that influence the reflex arc due to a suprasegmental lesion, that is, a lesion above the level of the spinal reflex pathways By convention the deep tendon reflexes are graded as follows 0 = no response; · Results Of the 225 surgically treated patients, a Hoffmann sign occurred in 68%, hyperreflexia in 60%, and Babinski sign in 33% In patients with milder disability (mJOA Scores 14–16), the Hoffmann sign was present 46%, whereas a Babinski sign occurred in 10%;
Fundamentals Of Cervical Neurological Exam Springerlink
Positive hoffman's sign and hyperreflexia
Positive hoffman's sign and hyperreflexia-3101 · Hyperreflexia is a consequence of loss of inhibition from descending motor tracts The Babinski's and Hoffmann's signs are special examples of loss of inhibition Spasticity, which is a disorder of deep tendon reflex loops, is a companion of hyperreflexiaHe has hyperreflexia in the UE's and LE's and has a positive Hoffman's sign, positive Babinski sig This gentleman has questionable cervical cord compression




Neurological Signs In Medicine
· A positive Hoffman sign indicates an upper motor neuron lesion and corticospinal pathway dysfunction likely due to cervical cord compression However, up to 3% of the population has been found to have a positive Hoffman without cord compression or upper motor neuron disease Issues of Concern While the Hoffman sign can help as a screening tool, it is not reliableA Hoffmann reflex can also happen in the presence of generalized hyperreflexia (overactive reflexes) as seen with anxiety or hyperthyroidism However, this test is not foolproof as the patients who don't have cervical myelopathy can have a positive Hoffmann sign A positive Hoffmann sign may be seen in patients with hyperthyroidism, anxiety disorders, and other conditions thatThis means that if a patient comes in with subtle signs of the disorder, using the Hoffmann sign, doctors may be able to make the diagnosis earlier than if waiting to rely on the Babinski sign The authors did point out, however, that there may be other reasons for a positive Hoffmann sign, such as in people with hyperreflexia , where the reflexes are much more active than in the
Here is a video of a patient with a positive Hoffman's sign and hyperreflexia with cervical spinal stenosis She also has some incoordination issues affectin She also has some incoordination · A positive finger flexor response elicited in this manner is known as the Hoffmann reflex or sign The doctor holds the middle finger while partially flexing itCauses The most common cause of hyperreflexia is spinal cord injury (see autonomic
Always abnormal 1 = a slightHyperreflexia, Clonus and a Positive Hoffman's Sign Hyperreflexia, Clonus and a Positive Hoffman's Sign Watch later Share Copy link Info Shopping Tap toI am a 28 year old female whom has Hoffman's sign, knee clonus, and hyperreflexia My neurologist hasn't a clue as to what is causing all of my symptoms I forget entire conversations I forget where I am I have severe muscle spasms/twitching and muscle weakness in my legs, and my arms are slowly weakening as well I choke on food and am now




Neurological Signs In Medicine




Bilateral Finger Jerks As A Useful Sign For Diagnosis Of Cervical Compressive Myelopathy Kasahata Journal Of Neurology Research
· hoffman's sign MedHelp's hoffman's sign Center for Information, Symptoms, Resources, Treatments and Tools for hoffman's sign Find hoffman's sign information, treatments for hoffman's sign and hoffman's sign symptomsResults Of the 225 surgically treated patients, a Hoffmann sign occurred in 68%, hyperreflexia in 60%, and a Babinski sign in 33% In patients with milder disability (mJOA Scores 1416), the Hoffmann sign was present in 46%, whereas a Babinski sign occurred in 10%; · I am a 47 year old female who three years ago herniated a disc at the T1T2 level which was deforming the spinal cord I saw a neurosurgeon at the time who recommended physiotherapy but stated that I should contact a neurologist as he noticed that "Hoffman Sign", "Brisk Hyperreflexia" and Muscle twitching were present




Pin On Md Stuff




The Method Of Eliciting The Reflexes A Eliciting The Hoffman S Download Scientific Diagram
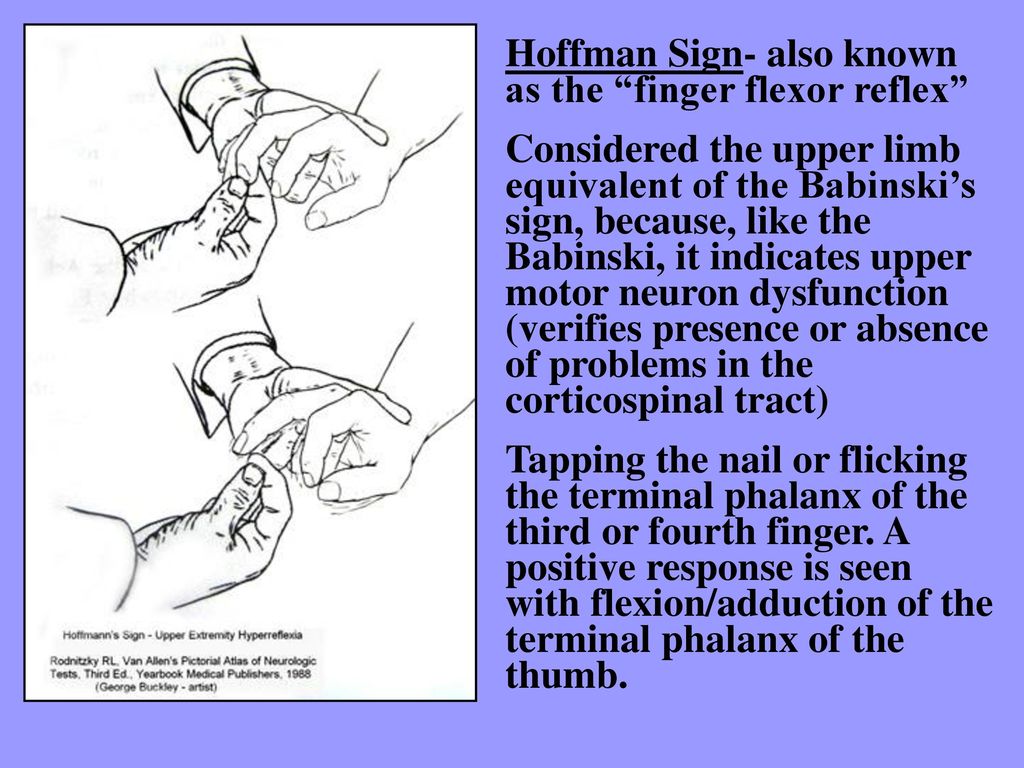
Clonus is a set of involuntary and rhythmic muscular contractions and relaxations Clonus is a sign of certain neurological conditions, particularly associated with upper motor neuron lesions involving descending motor pathways, and in many cases is, accompanied by spasticity (another form of hyperexcitability) Unlike small, spontaneous twitches known as fasciculations (usually caused by · The Hoffman sign indicates the presence of hyperreflexia It accompanies a variety of conditions, such as Hyperthyroidism, Some types of anxiety and other conditions related to deep tendon reflexes Hyperreflexia due to hyperthyroidism usually produces bilateral findingsHoffman's sign is a neurological sign in the hand which is an indicator of problems in the spinal cord It is associated with a loss of grip The test for Hoffman's sign involves tapping the nail on the third or forth finger A positive Hoffman's is the involuntary flexing of the end of the thumb and index finger normally, there should be no reflex response Hoffman's sign is an indicator of



Csiro Publishing Journal Of Primary Health Care




Hoffman S Sign Hyperreflexia And Positive Spurling S Test Youtube
In those with severe myelopathy and mJOA scores of ≤ 10, the Hoffmann sign was present in 81% and the Babinski sign in % · went to dr for clumsiness i had hyperreflexirms jaw jerk hoffman's sign babinski & clonus neuro ordered mri of brain what is she looking 4?3107 · Hyperreflexia of deep tendon reflexes The Hoffman sign is an analog of the Babinski reflex for the upper limbs The test is performed by loosely holding the patient's middle finger and quickly flicking the fingernail downward A positive sign is the flexion and adduction of the thumb PseudoBulbar Palsy As previously stated, most cranial nerves have bilateral




Hoffman S Sign What Do Positive And Negative Test Results Mean




Positive Hoffman S Sign And Hyperreflexia With Cervical Spinal Stenosis Youtube
Those with diabetes also had a significantly higher incidence of hyporeflexia and a higher incidence of a positive Babinski sign, but there was no difference in the appearance of the Hoffman sign The magnitude of mJOA improvement after surgery was comparable We conclude that diabetes may alter the typical signs and symptoms of cervical spondylotic myelopathy and suggest that · He interpreted the presence of a positive Hoffmann sign as a sign of hyperreflexia The sign was first described in the literature in 1911 by his student Hans Curschmann, who named the sign after Hoffmann The Hoffmann sign is a reflex that is now routinely included in standard neurological examinations A positive (abnormal) Hoffmann sign is considered to be suggestiveThe neurological examination was consistent with cervical myelopathy upper thoracic spinothalamic sensory level (%), hyperreflexia (64%), inversion of the radial periosteal reflex (57%), positive Romberg sign (28%), ankle clonus (25%), positive Hoffman sign (26%), impaired tandem walk (23%), dysmetria (15%) and dysdiadochokinesia (13%) MRI and contrastenhanced



Pyramidal Voluntary Motor System Ppt Download




Neurological Signs In Medicine



コメント
コメントを投稿